nf-core/hgtseq
A pipeline to investigate horizontal gene transfer from NGS data
1.0.0). The latest
stable release is
1.1.0
.
Introduction
nf-core/hgtseq is a bioinformatics best-practice analysis pipeline built to investigate horizontal gene transfer from NGS data.
The pipeline uses metagenomic classification of paired-read alignments against a reference genome to identify the presence of non-host microbial sequences within read pairs, and to infer potential integration sites into the host genome.
The pipeline is built using Nextflow, a workflow tool to run tasks across multiple compute infrastructures in a very portable manner. It uses Docker/Singularity containers making installation trivial and results highly reproducible. The Nextflow DSL2 implementation of this pipeline uses one container per process which makes it much easier to maintain and update software dependencies. Where possible, these processes have been submitted to and installed from nf-core/modules in order to make them available to all nf-core pipelines, and to everyone within the Nextflow community!
On release, automated continuous integration tests run the pipeline on a full-sized dataset on the AWS cloud infrastructure. This ensures that the pipeline runs on AWS, has sensible resource allocation defaults set to run on real-world datasets, and permits the persistent storage of results to benchmark between pipeline releases and other analysis sources. The results obtained from the full-sized test can be viewed on the nf-core website.
Functionality Overview
A graphical view of the pipeline can be seen below.
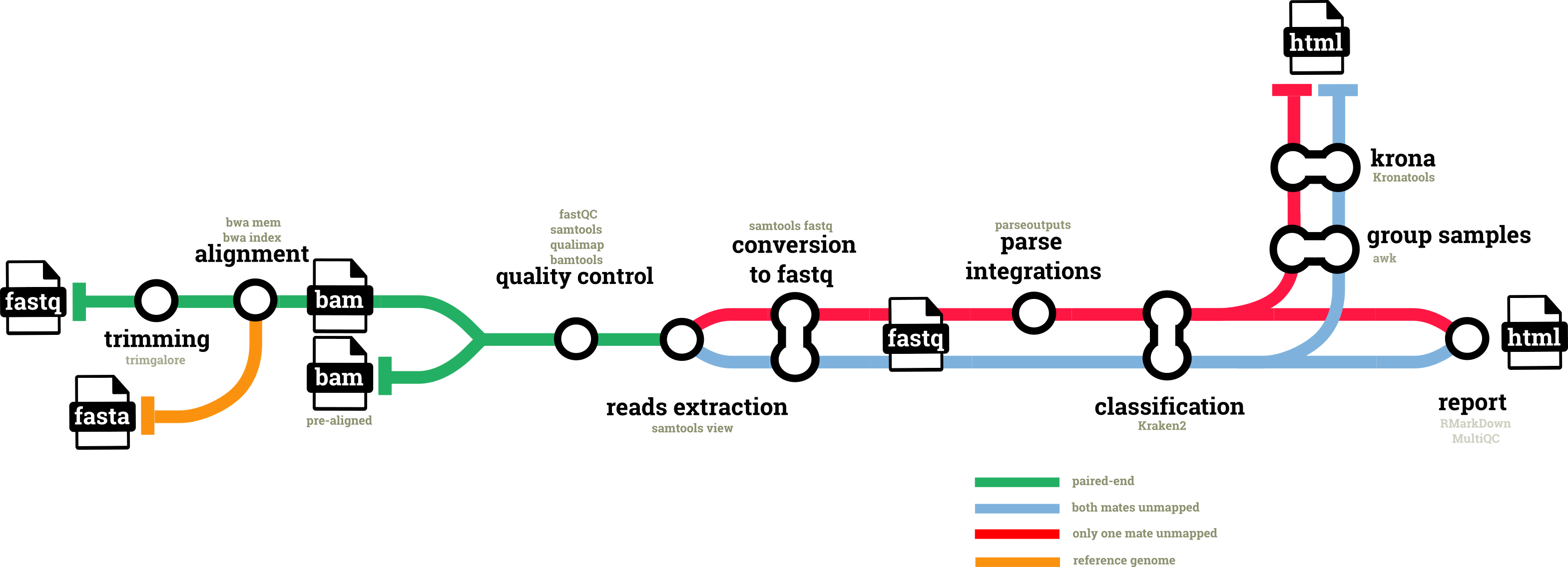
Pipeline summary
- Read QC (
FastQC) - Present QC for raw reads (
MultiQC) - Adapter and quality trimming (
Trim Galore) - Mapping reads using BWA (
BWA) - Sort and index alignments, extraction reads by sam flag and conversion to fastq format(
SAMtools) - Taxonomic classification (
Kraken2) - Plotting Kraken2 results (
Krona) - Html analysis report (
RMarkDown)
Quick Start
-
Install
Nextflow(>=21.10.3) -
Install any of
Docker,Singularity(you can follow this tutorial),Podman,ShifterorCharliecloudfor full pipeline reproducibility (you can useCondaboth to install Nextflow itself and also to manage software within pipelines. Please only use it within pipelines as a last resort; see docs). -
Download the pipeline and test it on a minimal dataset with a single command:
- FASTQ input:
nextflow run nf-core/hgtseq -profile test,YOURPROFILE --outdir <OUTDIR>- BAM input:
nextflow run nf-core/hgtseq -profile test_bam,YOURPROFILE --outdir <OUTDIR>
Note that some form of configuration will be needed so that Nextflow knows how to fetch the required software. This is usually done in the form of a config profile (YOURPROFILE in the example command above). You can chain multiple config profiles in a comma-separated string.
- The pipeline comes with config profiles called
docker,singularity,podman,shifter,charliecloudandcondawhich instruct the pipeline to use the named tool for software management. For example,-profile test,docker.- Please check nf-core/configs to see if a custom config file to run nf-core pipelines already exists for your Institute. If so, you can simply use
-profile <institute>in your command. This will enable eitherdockerorsingularityand set the appropriate execution settings for your local compute environment.- If you are using
singularity, please use thenf-core downloadcommand to download images first, before running the pipeline. Setting theNXF_SINGULARITY_CACHEDIRorsingularity.cacheDirNextflow options enables you to store and re-use the images from a central location for future pipeline runs.- If you are using
conda, it is highly recommended to use theNXF_CONDA_CACHEDIRorconda.cacheDirsettings to store the environments in a central location for future pipeline runs.
-
Start running your own analysis!
nextflow run nf-core/hgtseq \ --input <YOURINPUT>.csv \ --outdir <OUTDIR> \ --genome GRCh38 \ --taxonomy_id "TAXID" \ -profile <docker/singularity/podman/shifter/charliecloud/conda/institute> \ --krakendb /path/to/kraken_db \ --kronadb /path/to/krona_db/taxonomy.tab
Documentation
The nf-core/hgtseq pipeline comes with documentation about the pipeline usage, parameters and output.
Credits
nf-core/hgtseq was originally written by Simone Carpanzano, Francesco Lescai.
We thank nf-core community, and in particular the authors of the modules used in the pipeline: Paolo Cozzi, Jose Espinosa-Carrasco, Phil Ewels, Gisela Gabernet, Maxime Garcia, Jeremy Guntoro, Friederike Hanssen, Matthias Hortenhuber, Patrick Hüther, Suzanne Jin, Felix Krueger, Harshil Patel, Alex Peltzer, Abhinav Sharma, Gregor Sturm, James Fellows Yates.
Contributions and Support
If you would like to contribute to this pipeline, please see the contributing guidelines.
For further information or help, don’t hesitate to get in touch on the Slack #hgtseq channel (you can join with this invite).
Citations
An extensive list of references for the tools used by the pipeline can be found in the CITATIONS.md file.
You can cite the nf-core publication as follows:
The nf-core framework for community-curated bioinformatics pipelines.
Philip Ewels, Alexander Peltzer, Sven Fillinger, Harshil Patel, Johannes Alneberg, Andreas Wilm, Maxime Ulysse Garcia, Paolo Di Tommaso & Sven Nahnsen.
Nat Biotechnol. 2020 Feb 13. doi: 10.1038/s41587-020-0439-x.